Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the thyroid gland, leading to excessive stimulation of the thyroid and consequent. This results in a range of symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and exophthalmos. While clinical evaluation and hormonal and antibody analysis are essential for diagnosing Graves' disease, sonographic imaging has become an invaluable tool for providing typical diagnostic features and exclusion of differentials.
Sonographic Techniques:
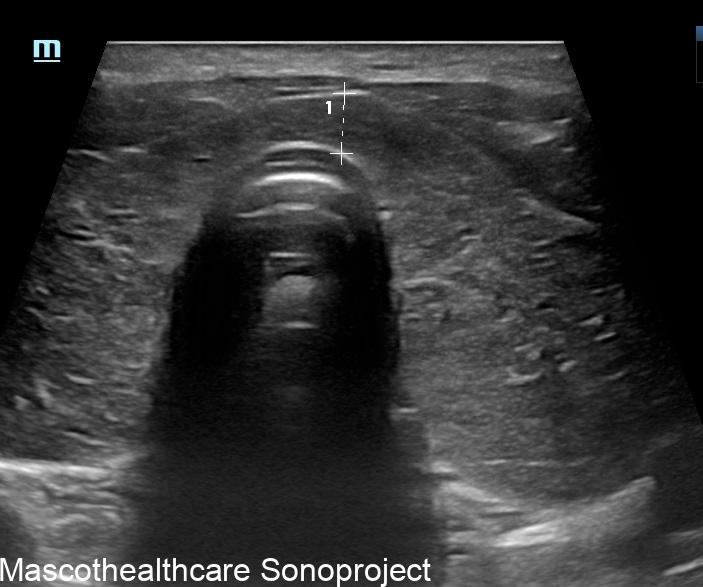
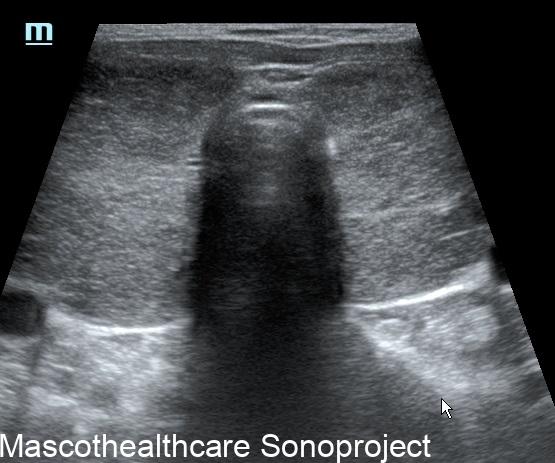
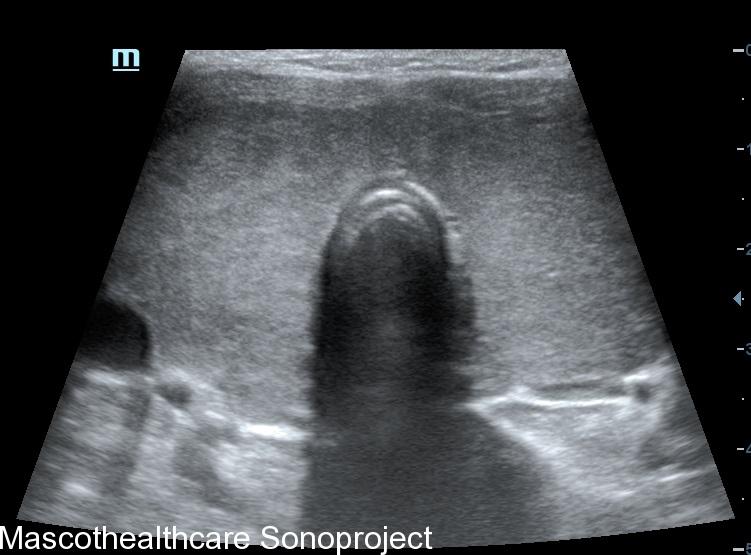
- B-mode Ultrasound: B-mode ultrasound don with an high frequency linear provides a detailed two-dimensional image of the thyroid gland. It helps in visualizing the gland's size, echogenicity and the presence of any nodules or abnormalities. In Graves' disease, the thyroid gland is often diffusely enlarged, gently lobulated outline, devoid of nodules with a coarse echotexture.
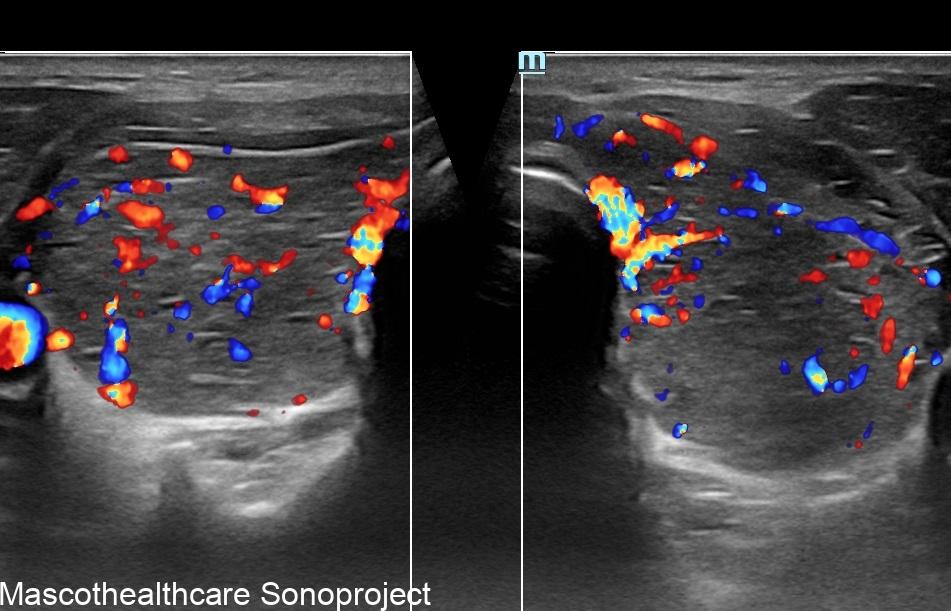
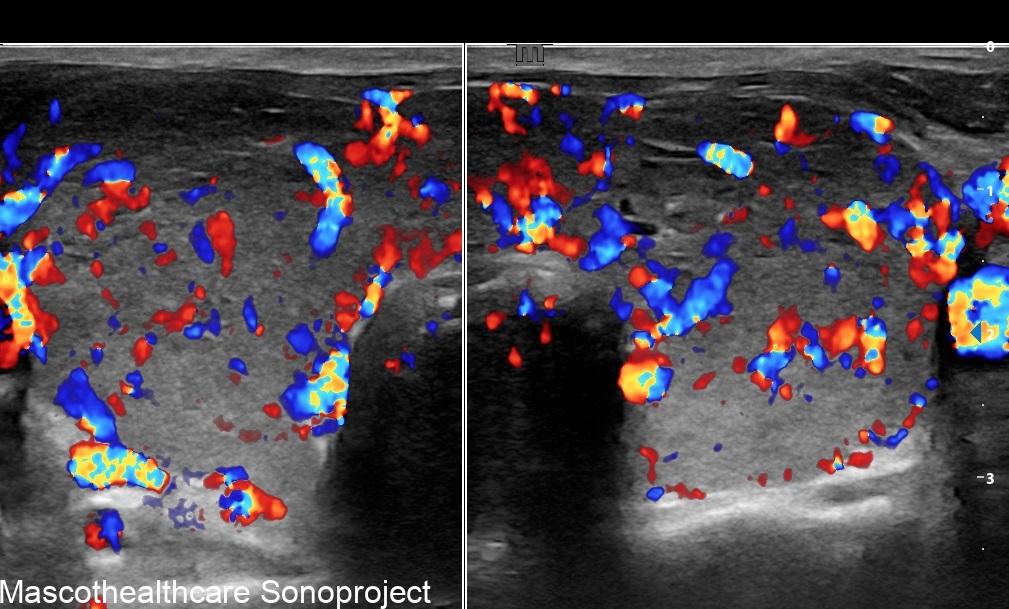
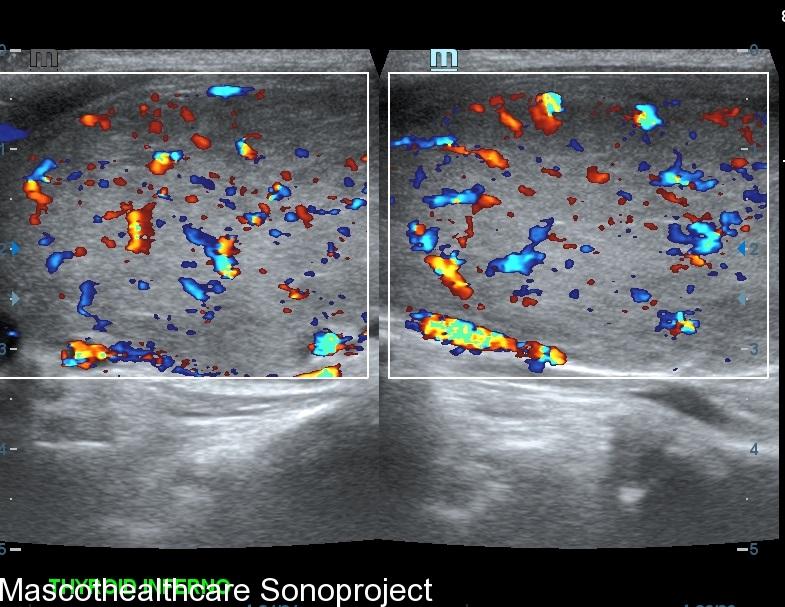
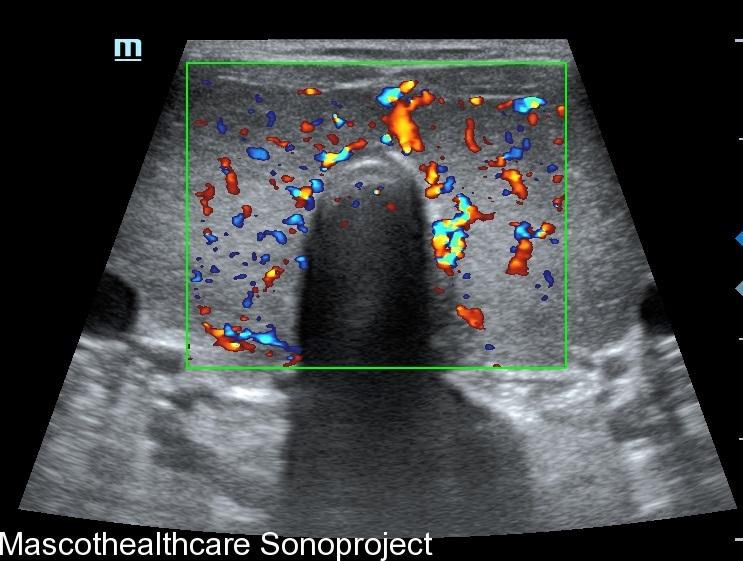
- Doppler Ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound is employed to assess blood flow within the thyroid gland. In Graves' disease, increased vascularity is a hallmark feature, and Doppler ultrasound helps visualize this by detecting elevated blood flow. The "thyroid inferno" pattern, indicative of intense blood flow on color doppler, is often observed in patients with Graves' disease. Autoimmune thyroiditis may also demonstrate increased vascularity in the acute phase however usually not as marked and persistent as that of Graves'.
Clinical Implications:
- Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis: Sonographic evaluation aids in confirming the diagnosis of Graves' disease and differentiating it from other thyroid disorders such nodular goiter or autoimmune Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The characteristic findings, such as diffuse enlargement and increased vascularity, contribute to a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
- Treatment Monitoring: Following the initiation of treatment, sonographic assessments can be employed to monitor the response to therapy. Reduction in thyroid size and vascularity can be indicative of treatment success.
- Guidance for Procedures: In cases where fine-needle aspiration (FNA) or biopsy is warranted, sonography helps guide these procedures accurately, ensuring that the sampled tissue is representative of the abnormal areas within the thyroid gland.