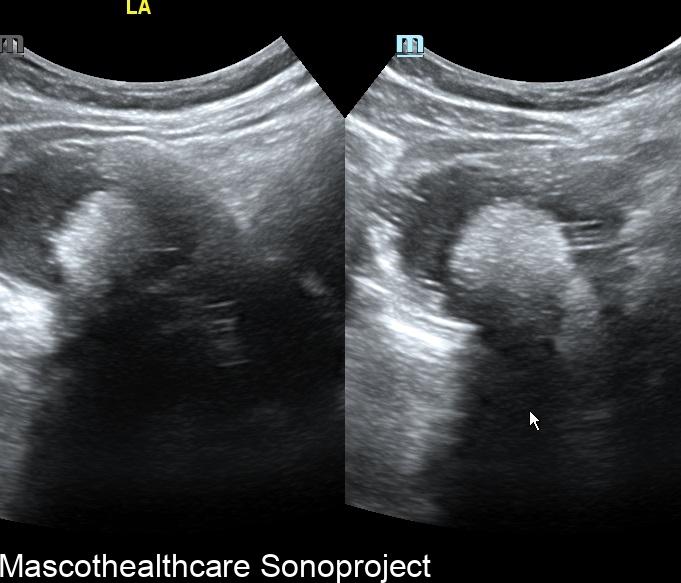
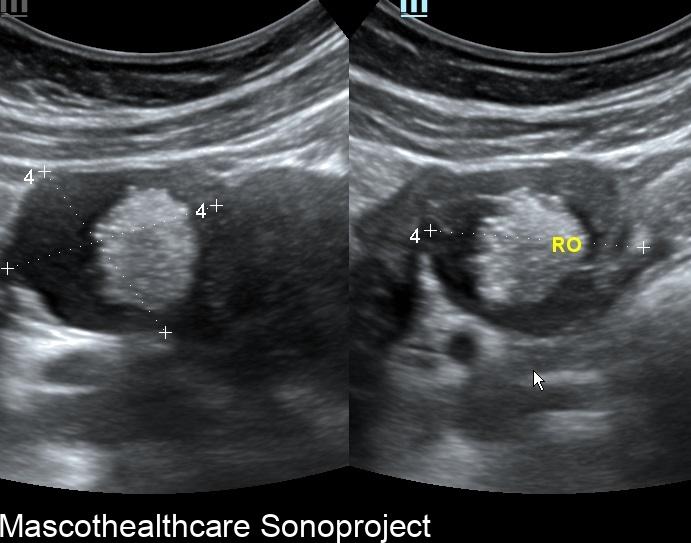
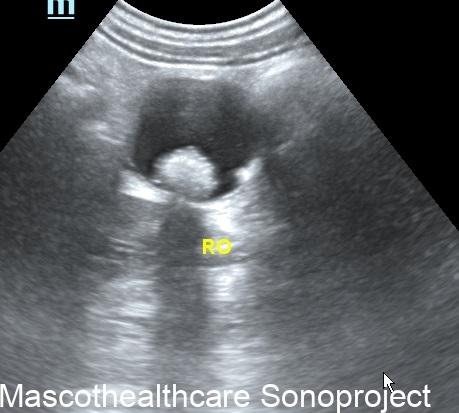
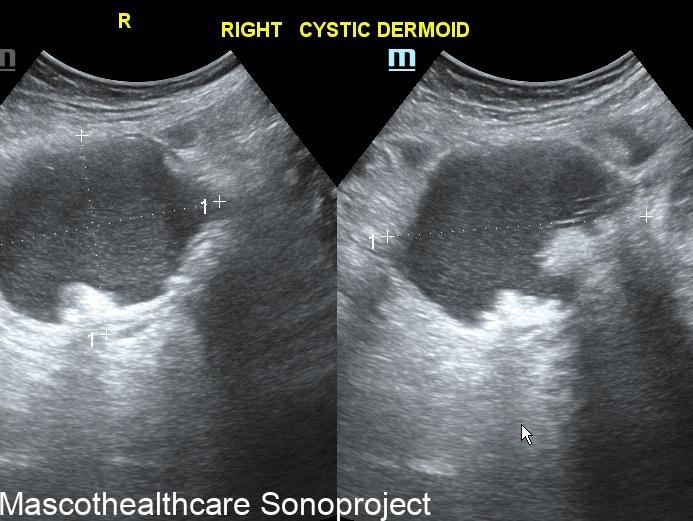
Dermoid cysts, also known as mature cystic teratomas, are common ovarian neoplasms arising from germ cells. Characterized by their diverse tissue composition, including skin, hair, and sebaceous material, dermoid cysts are typically benign. Ultrasound imaging plays a pivotal role in their diagnosis, offering insights into the cyst's morphology and aiding in appropriate clinical management.
Ultrasound Features:
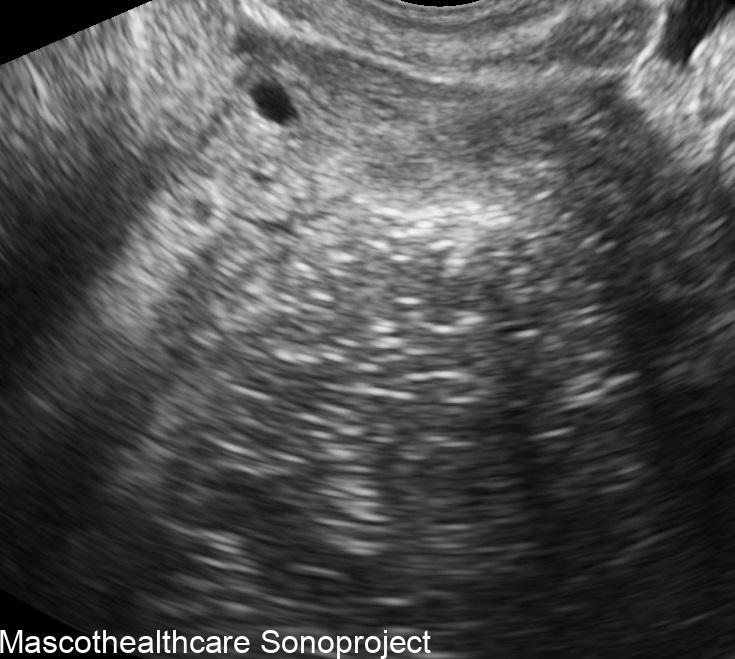
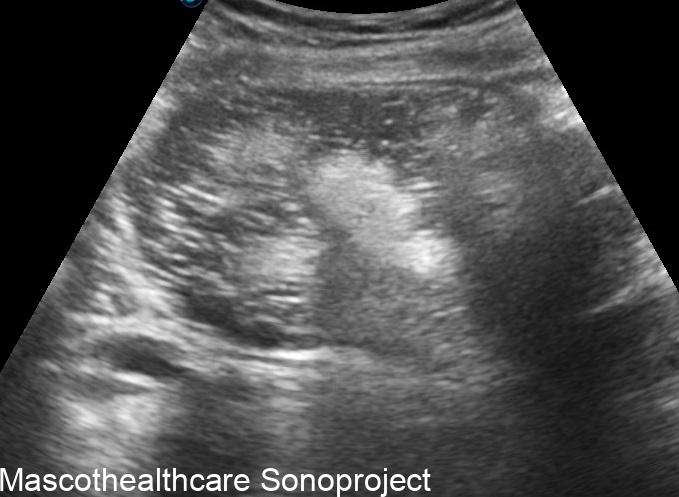
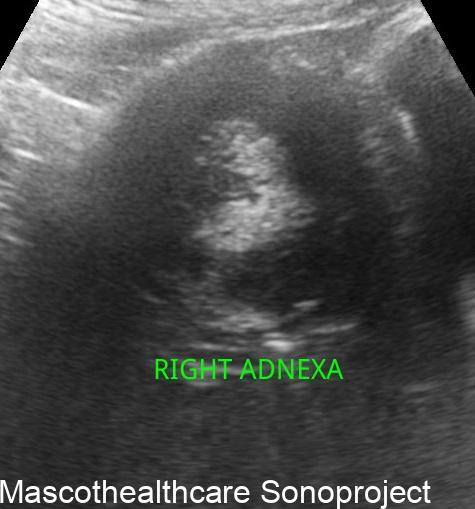
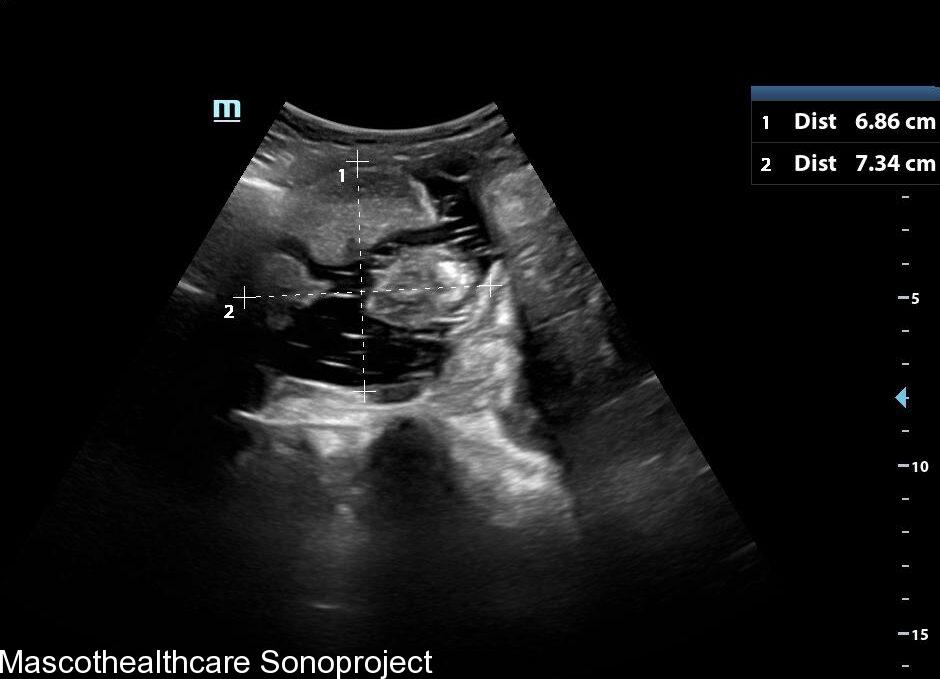
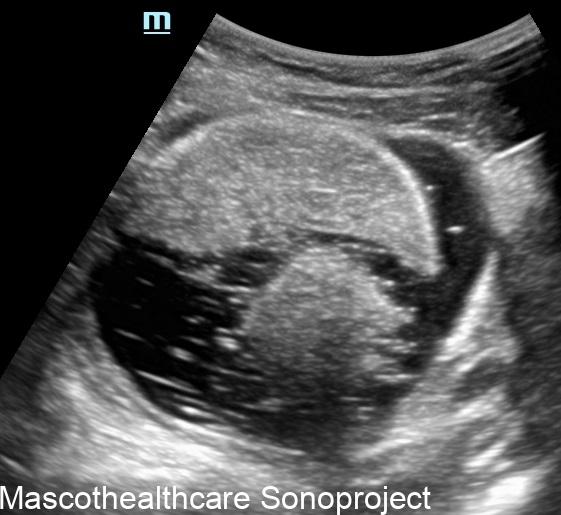
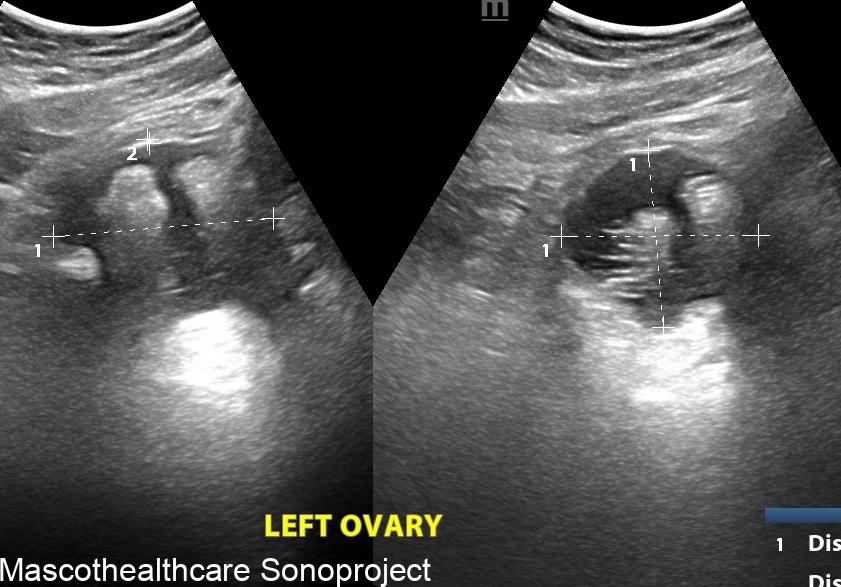
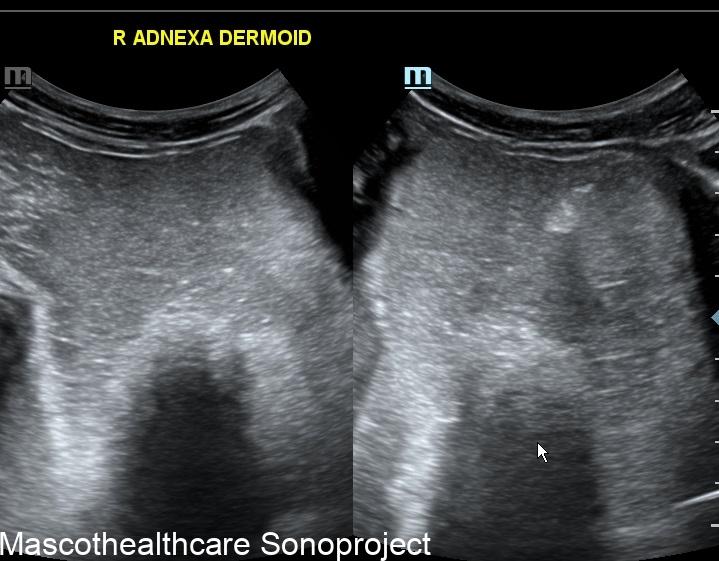
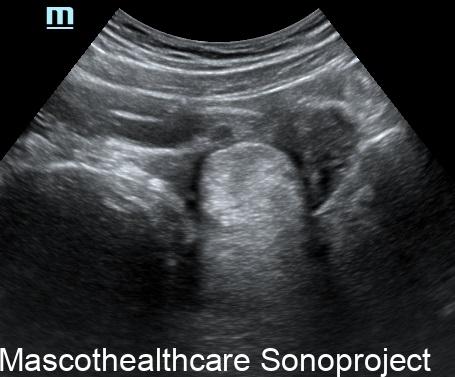
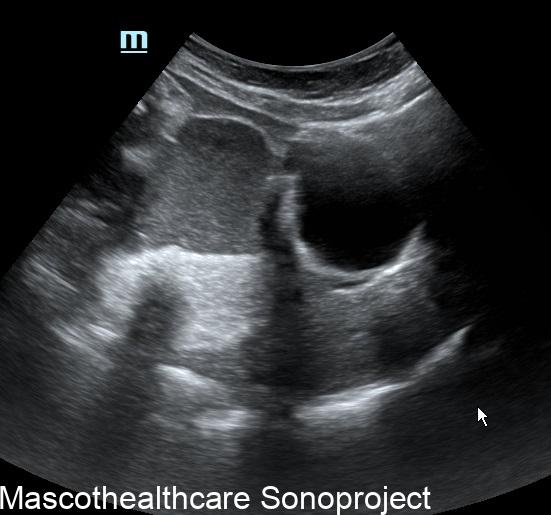
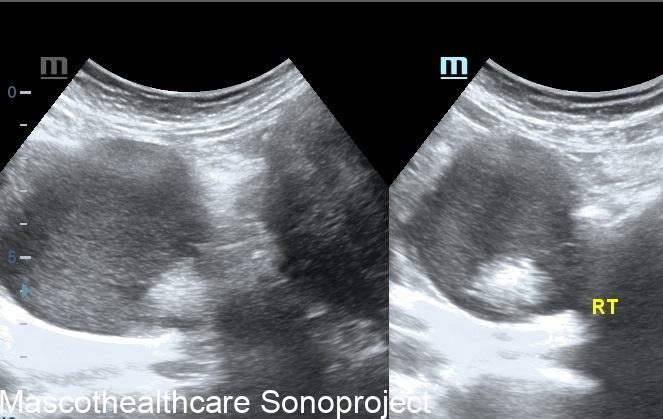
- Complex Cystic Structure: Dermoid cysts present as well-defined, complex cystic lesions on ultrasound. These structures often exhibit a combination of echogenic and hypoechoic regions.
- Tip of the Iceberg Sign: A distinctive feature of dermoid cysts is the "tip of the iceberg" appearance. This term describes the mobile internal echoes within the cyst, representing hair or sebaceous material. These echoes move with changes in the patient's position, adding a dynamic element to the ultrasound findings.
- Echogenic Nodules: Dermoid cysts may contain echogenic nodules, which correspond to calcifications or denser structures within the cyst. These nodules contribute to the cyst's heterogeneous echotexture.
- Minimal Vascularity: Color Doppler imaging of dermoid cysts typically reveals minimal to no blood flow within the lesion. This lack of vascularity is a useful diagnostic clue differentiating dermoid cysts from other ovarian masses.
Clinical Implications: Accurate identification of dermoid cysts through ultrasound is crucial for appropriate clinical management. In cases where characteristic features are present and the cyst remains asymptomatic, a conservative approach with regular monitoring may be warranted. This strategy helps avoid unnecessary surgical interventions, considering the benign nature of these cysts.
Management Options: The decision to intervene surgically is often guided by the presence of symptoms, rapid cyst growth, or the development of concerning features during follow-up imaging. Surgical options include cystectomy or oophorectomy, depending on the patient's age, reproductive goals, and the cyst's characteristics.